Seamless mobility in smart cities
Transforming urban traffic through micromobility
In their efforts to drive sustainable mobility, cities are devoting increasingly emphasizing the importance of what is called "micromobility". Infineon's semiconductor solutions enable efficient energy consumption as well as seamless and intelligent service ranges with Mobility as a Service (MaaS) for both the emerging light electric vehicles themselves and for their integration into mobility service platforms.
E-bike, e-scooter, e-skateboard
Versatile vehicles for a seamless mobility experience

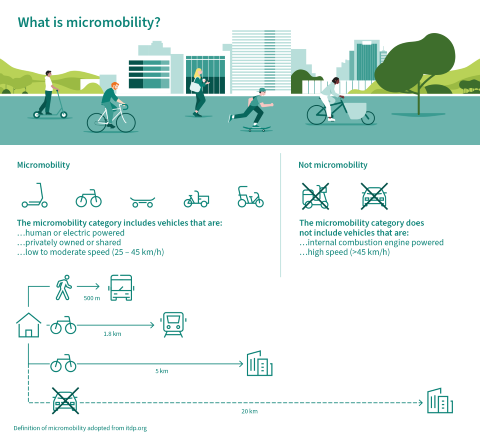
Micromobility is based on small, lightweight devices operating at speeds usually below 25 km/h and focuses on short distances. It includes small and light weight electrical vehicles such as e-scooters, e-bikes, e-rikshaws and e-cargo bikes.
These means of transport offer a well-connected seamless mobility experience for residents and visitors, reducing car traffic, noise and pollution. Due to their flexibility and widespread availability, they provide better access to more places for more people and can complement public transport.
A prerequisite for the success of micromobility concepts is that cities continue to build safe corridors for micromobility such as cycle highways, bike lanes and mixed-traffic streets with speed limits. And micromobility is by no means limited to private transport: Commercial transportation increasingly uses Light Electric Vehicles (LEV) such as parcel deliverers on e-cargo bikes and meal deliverers on e-bikes.
Last mile e-mobility
Powering efficient light electrical vehicles with semiconductors

When we talk about micromobility, we are referring to smaller vehicles with electric drivetrains, such as e-scooters.
They are referred to the term Light Electric Vehicles (LEV). Which vehicles are covered by this term varies among publications and countries.
By definition, LEVs weigh less than 750 kg and have a maximum power of 15 kW and maximum speeds of less than 100 km/h such as e-mopeds, small delivery e-trucks, e-robots.
They offer several benefits: First, they allow users to move around as they wish to: drive on roads, move along sidewalks or to get around inside large buildings such as factories. Secondly, they are electrically powered, which is climate friendly, as long as they use renewable energy. And: The small size of the vehicles helps ease traffic congestion and parking space shortages. Infineon empowers the manufacturers as a partner of choice in developing electric light vehicle technologies. We offer products not only for the vehicles themselves, but also the battery chargers, charging/swapping stations and even the batteries.
Read more about what LEVs are and how they are categorized
Shared mobility services
Unfolding the magic with shared mobility services

The great charm of micromobility lies not only in the versatility and flexibility of the different vehicle types. Micromobility's true fascination unfolds in particular when the vehicles are embedded in mobility service platforms: People can rent and use a vehicle on demand and enjoy shared mobility in addition to the private ownership of a vehicle. Service platforms that intelligently integrate such various means of transport into a single service offer are categorized as Mobility as a Service (MaaS).
MaaS concepts and apps drive sustainable mobility, make urban traffic smarter and respond to the growing desire for seamless, green and personal mobility, including the best possible connection to public transportation. They let users plan, book and pay for the best point-to-point travel across modes. Infineon is a key enabler for the rise of MaaS ranges by pushing for open standards, highest safety, trusted payment solutions and breakthrough technologies such as ultra-wideband.
Read more about Mobility as a Service
Infineon India’s Pune Center of Competence for electric two and three wheelers
India has emerged as the world’s biggest two-wheeler market.
That’s why Infineon has set up the Center of Competence (CoC) for two and three wheelers in Pune as a unique system application lab for global Infineon Technologies. It deals with new regulations on emissions and safety, progress in electrification and electric drives as well as growing customer demand. The CoC has specific objectives:
- Develop innovative system solutions for two and three wheelers with advanced technology and products to address customer pain points and reduce time-to-market
- Validate new products and solutions in real-world applications, understand application requirements in order to address product gaps
- Build system expertise in two and three wheeler EV applications for enhanced global technical customer support and build trust-based customer partnerships
Delivery robots expand and complement progressive forms of mobility
Autonomous delivery robots are a promising field for logistics companies, retailers, and customers alike. While the delivery robots market is still in its infancy, the demand for these everyday helpers is already growing rapidly.

Specialized companies, many of them in Asia, are leading the way, pioneering safety standards and eventually mass production. The main reason for the significant increase in the development of delivery robots is consumer desire for quick deliveries.
Depending on the area of application, there are different robot types. For example, delivery robots, which are comparatively slow, unmanned or transporting food or other items. They are perfect for last-mile delivery. They also feature good battery life, store and transmit service information to users and use precise sensors to perform particularly demanding tasks.
Infineon provides all the electronics for these types of service robots and enables robot developers to overcome technical challenges with the help of the next generation of semiconductor technologies.
Highlights from Infineon’s portfolio include OPTIGATM Trust, OptiMOSTM, MOSFETs, gate driver ICs and DC/DC controllers.