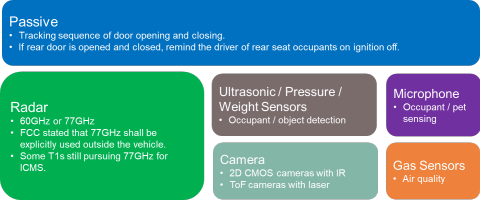
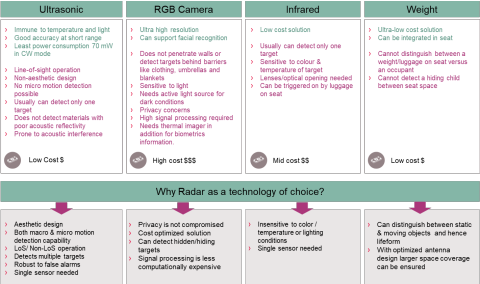
Occupant monitoring system (OMS)
The concept of occupancy monitoring systems (OMS) is relatively new compared to driver monitoring systems. The information from these systems can be used for turning on seat heating, seat belt alarm detection, smart airbag deployment, left-behind life warnings, automated air conditioning systems, and many more.
Scalable in-cabin monitoring systems with our 60 GHz radar solutions
Infineon's scalable solutions support the evolving in-cabin monitoring system requirements and regulations that are evolving. Having a scalable solution enables cost-effective core designs, provides flexibility for being adapted, and reducing development costs and time to market.
- Occupant classification
- Child presence detection
- Vital signs and health monitoring
- Seat occupancy detection and reminder
- Intrusion detection and alert
- Smart airbags
60 GHz radar sensors for in-cabin monitoring with highest performance
Using Infineon automotive products enables best-in-class performance for your design: from low-noise supply concepts, 60 GHz radar MMIC specifically designed for short-range applications, and high-performance microcontrollers with a dedicated processing unit optimized for radar signals.
Infineon's expertise in automotive radar products and applications
Infineon is an industry leader in automotive radar systems with many years of experience in this high-growth market. Infineon's automotive radar product and application expertise and experience combined with our selected design house partners give our customers the confidence of working with a trusted partner.
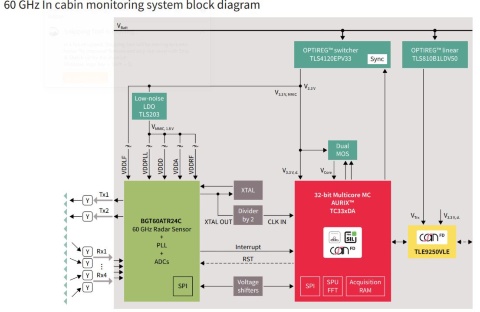
In-cabin sensing is a newly emerging market, which is expected to see a potential boost due to regulations and legislations worldwide. Radar is seen as one of the promising technologies to address not only passive safety applications like left-behind child detection or occupancy sensing. Novel signal processing techniques will potentially take these applications to a next level of robustness providing a good compromise between computational costs, degree of information needed for use-case as well as the power consumption of the system. In the future, the multi-sensor fusion approach is expected to penetrate much more robust systems by offering sensor redundancy.