Silicon-on-insulator (SOI) Gate Driver ICs
SOI level-shift high-voltage gate driver ICs for IGBTs and MOSFETs
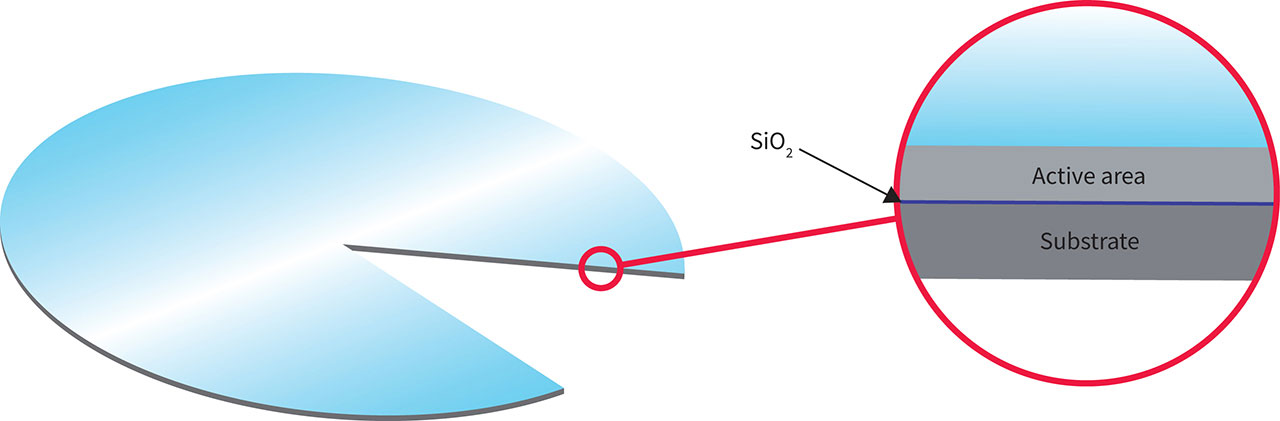
Our silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology is a high-voltage, level-shift technology providing unique, measurable and best-in-class advantages, including integrated bootstrap-diode (BSD) and industry best-in-class robustness to protect against negative transient voltage spikes. Each transistor is isolated by buried silicon dioxide, which eliminates the parasitic bipolar transistors that causing latch-up. This technology can also lower the level-shift power losses to minimize device-switching power dissipation. The advanced process allows monolithic high-voltage and low-voltage circuitry construction with technology-enhanced benefits.
Now including the 2ED218x - high current 650 V, 2.5 A, half-bridge SOI gate driver family, and new 2ED210x - low current 650 V, 0.7 A, half-bridge SOI gate driver family. Both product families include two package options of DSO-8 and DSO-14.
Silicon on insulator (SOI) technology
Our silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology is a high-voltage, level-shift technology for gate driver ICs with integrated bootstrap-diode (BSD) and industry-best-inclass robustness to protect against negative transient voltage spikes. Each transistor is isolated by buried silicon dioxide eliminating parasitic bipolar transistors that can cause latch-up. This technology can also lower the level-shift power losses to minimize device-switching power dissipation. The advanced process allows monolithic high-voltage and low-voltage circuitry construction with technology-enhanced benefits.
We offer three-phase and half-bridge gate driver ICs that can drive up to 8 A current and withstand voltages for each voltage class: <200 V, 600 V, 650 V, and 1200 V.
Main benefit of our SOI: Immunity to negative transient voltage
Today's high-power switching inverters and drives carry a large load current. The voltage swing on the VS pin does not stop at the level of the negative DC bus. It swings below the level of the negative DC bus due to the parasitic inductances in the power circuit and from the die bonding to the PCB tracks. This undershoot voltage is called "negative transient voltage". EiceDRIVER™ high-voltage level-shift gate driver IC products using Infineon SOI technology have the best-in-the-industry operational robustness.
For example, consider the negative Vs transient safe operating area (SOA) chart of an SOI gate driver such as 6ED2230S12T - which can be found in the datasheet. At VBS = 15 V and for negative VS transients of -80V, the product can withstand pulse widths up to 1000 ns without showing unwanted functional anomalies or permanent damage to the IC.
Main benefit of Infineon SOI: Integrated, low-ohmic bootstrap diode
The bootstrap power supply is one of the most common techniques for supplying power to the high-side driver circuitry due to its simplicity and low cost.
The bootstrap power supply consists of a bootstrap diode and capacitor. The floating channel of level-shift gate drivers is typically designed for bootstrap operation. Infineon SOI drivers feature excellent integrated ultra-fast bootstrap diodes. The low diode resistance of RBS ≤40 Ω enables a wide operating range.
The Infineon SOI drivers with this feature can drive larger IGBTs without the risk of self-heating, minimizing BOM count and reducing system cost.
Main benefit of Infineon SOI: Low level-shift losses
Level-shift losses contribute significantly when the operating frequency increases. A level-shift circuit is used to transmit the switching information from the low side to the high side. The necessary charge of the transmission determines the level-shift losses.
EiceDRIVER™ high-voltage level-shift gate driver ICs using Infineon SOI technology require a very low charge to transmit the information. Minimizing level-shifting power consumption allows design flexibility of higher frequency operations, as well as a longer lifetime, improved system efficiency, and application reliability.
When testing an Infineon SOI gate driver(2ED2106S06F) versus standard gate driver (DC Bus voltage = 300 V; With CoolMOS™ P7 in D-Pak; 300 kHz switching frequency), the thermal diagrams indicate a temperature difference of 55.6°C lower in the power dissipation of the Infineon SOI-based products. Thermal diagrams are avaialble in the Gate Driver IC Selection Guide.
Additionally, EVAL-2ED2101-HB-LLC is an evaluation board demonstrating the low level-shift losses benefit of Infineon SOI in a fast-switching LLC power stages with resonant-tank with switching frequencies in the 500 kHz range.
Operation robustness of negative transient voltage at the VS pin (-VS)
Today's high-power switching inverters and drives carry a large load current. The voltage swing on VS pin does not stop at the level of the negative DC bus. It swings below the level of the negative DC bus due to the parasitic inductances in the power circuit and from the die bonding to the PCB tracks. This undershoot voltage is called "negative transient voltage".
EiceDRIVER™ high-voltage level-shift gate driver IC products using Infineon SOI technology have the best-in-the-industry operational robustness. In Below the safe operating line of a SOI gate driver (6ED2230S12T - coming soon) is shown at VBS = 15 V for pulse widths up to 1000 ns. In the green area, the products do not show unwanted functional anomalies or permanent damage to the IC.
*coming soon
Minimize your costs with compact solutions that offer bigger benefits! Discover Infineon's new 650 V 6EDL04 gate driver, featuring a strong negative Vs capability to prevent malfunctions and a higher voltage rating for better handling of DC bus voltage transients. This product combines higher voltage ratings with best-in-class robustness in a compact TSSOP-25 package. Join us to explore the new 6EDL04 family and its benefits.
This training features how the level-shift gate drivers work, what are negative voltage transient and how they affect level-shift gate drivers. In addition you will learn about the technology difference between Junction isolation and Infineon’s Silicon-On-Insulator technology.

You will have a glimpse of the different gate driver technologies available at Infineon and their benefits.
For a better understanding we will take a look at the optimization of external gate resistors to drive MOSFETs in a given application.
With this training, you will learn how to calculate a gate resistance value for an IGBT application, how to identify suitable gate driver ICs based on peak current and power dissipation requirements, and how to fine-tune the gate resistance value in laboratory environment based on worst case conditions.
We offer a large portfolio of level shift high voltage gate drivers – silicon-on-insulator (SOI) and junction isolated (JI) technologies. Learn about the advantages of Infineon SOI gate driver: integrated bootstrap diode, Low level-shift losses, saving space and cost, and negative VS robustness.